July 2018 Clinical Study
Videofluoroscopy
Hypertonia and aspiration
PHARYNGO-ESOPHAGEAL VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY
TECHNIQUE:
Videofluoroscopy is performed with semisolid bolus and liquid with videofluoroscopy recording. CBCT 2 D.
REASON FOR THE EXPLORATION:
- In Manometry May '14: incomplete relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter with signs of penetration into the airways, compatible with hypertrophy of the cricopharyngeus, it is also seen obstruction to esophago-gastric flow secondary to hiatal hernia.
- FGS: Esophageal motor disorder. Incipient muscular ring. Esophageal biopsies (AP: mild esophagitis).minimal sliding hiatal hernia.chronic gastritis.
- TEGD (Feb '14): esophageal motility alteration with absence of cricopharyngeal muscle relaxation, small hiatal hernia with mild GERD.
FINDINGS:
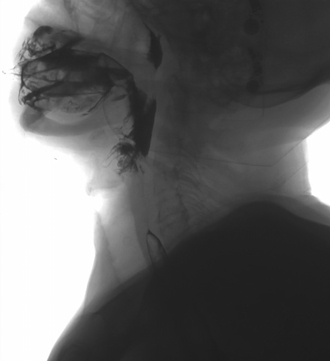
Oral phase: No oral containment.
Pharyngeal phase: Incomplete tension and elevation of the soft palate without retropalatal airspace coaptation but without pharyngonasal reflux.
Laryngeal ascent with epiglottic closure defect and presence of contrast material in the airway.
Upper esophageal sphincter opening phase: Incomplete relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter due to hypertrophy of the cricopharyngeus muscle.
Esophageal phase: normal esophageal clearance distal to the upper esophageal sphincter.
Assessment: There are several findings: On the one hand an incomplete relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter that hinders the progression of the semisolid bolus. With the liquid bolus, there are images of aspiration in the airway due to an incomplete closure of the epiglottis, correct progression of the liquid bolus in the upper esophageal sphincter.